chrome.webRequest
| Description: |
Use the chrome.webRequest API to observe and analyze traffic and to intercept, block, or modify requests in-flight.
|
| Availability: |
Since Chrome 35.
|
| Permissions: |
"webRequest"
host permissions |
Manifest
You must declare the "webRequest" permission in the extension manifest to use the web request API, along with the necessary host permissions. To intercept a sub-resource request, the extension needs to have access to both the requested URL and its initiator. If you want to use the web request API in a blocking fashion, you need to request the "webRequestBlocking" permission in addition. For example:
{
"name": "My extension",
...
"permissions": [
"webRequest",
"*://*.google.com/"
],
...
}
Life cycle of requests
The web request API defines a set of events that follow the life cycle of a web request. You can use these events to observe and analyze traffic. Certain synchronous events will allow you to intercept, block, or modify a request.
The event life cycle for successful requests is illustrated here, followed by
event definitions:
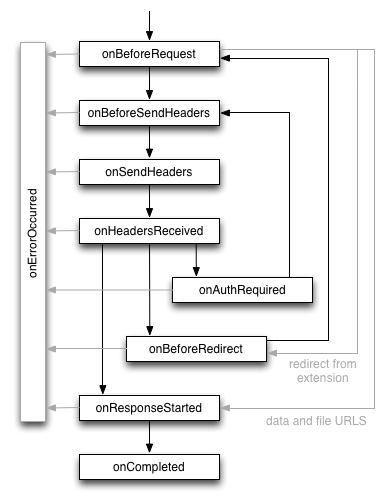
onBeforeRequest(optionally synchronous)- Fires when a request is about to occur. This event is sent before any TCP connection is made and can be used to cancel or redirect requests.
onBeforeSendHeaders(optionally synchronous)- Fires when a request is about to occur and the initial headers have been
prepared. The event is intended to allow extensions to add, modify, and delete
request headers (*). The
onBeforeSendHeadersevent is passed to all subscribers, so different subscribers may attempt to modify the request; see the Implementation details section for how this is handled. This event can be used to cancel the request. onSendHeaders- Fires after all extensions have had a chance to modify the request headers, and presents the final (*) version. The event is triggered before the headers are sent to the network. This event is informational and handled asynchronously. It does not allow modifying or cancelling the request.
onHeadersReceived(optionally synchronous)- Fires each time that an HTTP(S) response header is received. Due to redirects and authentication requests this can happen multiple times per request. This event is intended to allow extensions to add, modify, and delete response headers, such as incoming Content-Type headers. The caching directives are processed before this event is triggered, so modifying headers such as Cache-Control has no influence on the browser's cache. It also allows you to cancel or redirect the request.
onAuthRequired(optionally synchronous)- Fires when a request requires authentication of the user. This event can be handled synchronously to provide authentication credentials. Note that extensions may provide invalid credentials. Take care not to enter an infinite loop by repeatedly providing invalid credentials. This can also be used to cancel the request.
onBeforeRedirect- Fires when a redirect is about to be executed. A redirection can be triggered by an HTTP response code or by an extension. This event is informational and handled asynchronously. It does not allow you to modify or cancel the request.
onResponseStarted- Fires when the first byte of the response body is received. For HTTP requests, this means that the status line and response headers are available. This event is informational and handled asynchronously. It does not allow modifying or cancelling the request.
onCompleted- Fires when a request has been processed successfully.
onErrorOccurred- Fires when a request could not be processed successfully.
onCompleted or onErrorOccurred is fired as the final
event with one exception: If a request is redirected to a data://
URL, onBeforeRedirect is the last reported event.
(*) Note that the web request API presents an abstraction of the network stack to the extension. Internally, one URL request can be split into several HTTP requests (for example to fetch individual byte ranges from a large file) or can be handled by the network stack without communicating with the network. For this reason, the API does not provide the final HTTP headers that are sent to the network. For example, all headers that are related to caching are invisible to the extension.
The following headers are currently not provided to the
onBeforeSendHeaders event. This list is not guaranteed to be
complete nor stable.
- Authorization
- Cache-Control
- Connection
- Content-Length
- Host
- If-Modified-Since
- If-None-Match
- If-Range
- Partial-Data
- Pragma
- Proxy-Authorization
- Proxy-Connection
- Transfer-Encoding
Starting from Chrome 79, request header
modifications affect Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) checks. If modified
headers for cross-origin requests do not meet the criteria, it will result in
sending a CORS preflight to ask the server if such headers can be accepted.
If you really need to modify headers in a way to violate the CORS protocol, you
need to specify 'extraHeaders' in opt_extraInfoSpec.
On the other hand, response header modifications do not work to deceive CORS
checks. If you need to deceive the CORS protocol, you also need to specify
'extraHeaders' for the response modifications.
Starting from Chrome 79, the webRequest API
does not intercept CORS preflight requests and responses by
default. A CORS preflight for a request URL is visible to an extension if there
is a listener with 'extraHeaders' specified in
opt_extraInfoSpec for the request URL. onBeforeRequest
can also take 'extraHeaders' from Chrome 79.
Starting from Chrome 79, the following request
header is not provided and cannot be modified or removed
without specifying 'extraHeaders' in
opt_extraInfoSpec:
- Origin
Note: Modifying the Origin request header might
not work as intended and may result in unexpected errors in the response's
CORS checks. This is
because while extensions can only modify the
Origin request
header, they can't change the request origin or initiator, which is
a concept defined in the Fetch spec to represent who initiates the request. In
such a scenario, the server may allow the CORS access for the modified request
and put the header's Origin into the
Access-Control-Allow-Origin header in the response. But it won't
match the immutable request origin and result in a CORS failure.
Starting from Chrome 72, if you need to
modify responses before
Cross Origin Read Blocking (CORB)
can block the response, you need to specify 'extraHeaders' in
opt_extraInfpSpec.
Starting from Chrome 72, the following request
headers are not provided and cannot be modified or removed
without specifying 'extraHeaders' in
opt_extraInfoSpec:
- Accept-Language
- Accept-Encoding
- Referer
- Cookie
Starting from Chrome 72, the Set-Cookie
response header is not provided and cannot be modified or
removed without specifying 'extraHeaders' in
opt_extraInfoSpec.
Note: Specifying 'extraHeaders' in
opt_extraInfoSpec may have a negative impact on performance, hence
it should only be used when really necessary.
The webRequest API only exposes requests that the extension has
permission to see, given its
host permissions.
Moreover, only the following schemes are accessible:
http://,
https://,
ftp://,
file://,
ws:// (since Chrome 58),
wss:// (since Chrome 58), or
chrome-extension://.
In addition, even certain requests with URLs using one of the above schemes
are hidden. These include
chrome-extension://other_extension_id where
other_extension_id is not the ID of the extension to handle
the request,
https://www.google.com/chrome,
and other sensitive requests core to browser functionality. Also synchronous
XMLHttpRequests from your extension are hidden from blocking event handlers in
order to prevent deadlocks.
Note that for some of the supported schemes the set of available events might be
limited due to the nature of the corresponding protocol.
For example, for the file:
scheme, only onBeforeRequest,
onResponseStarted, onCompleted, and
onErrorOccurred may be dispatched.
Starting from Chrome 58, the webRequest API supports intercepting the WebSocket handshake request. Since the handshake is done by means of an HTTP upgrade request, its flow fits into HTTP-oriented webRequest model. Note that the API does not intercept:
- Individual messages sent over an established WebSocket connection.
- WebSocket closing connection.
Starting from Chrome 72, an extension will be able to intercept a request only if it has host permissions to both the requested URL and the request initiator.
Concepts
As the following sections explain, events in the web request API use request IDs, and you can optionally specify filters and extra information when you register event listeners.
Request IDs
Each request is identified by a request ID. This ID is unique within a browser session and the context of an extension. It remains constant during the the life cycle of a request and can be used to match events for the same request. Note that several HTTP requests are mapped to one web request in case of HTTP redirection or HTTP authentication.
Registering event listeners
To register an event listener for a web request, you use a variation on the
usual addListener() function.
In addition to specifying a callback function,
you have to specify a filter argument and you may specify an optional extra info
argument.
The three arguments to the web request API's addListener() have
the following definitions:
var callback = function(details) {...};
var filter = {...};
var opt_extraInfoSpec = [...];
Here's an example of listening for the onBeforeRequest
event:
chrome.webRequest.onBeforeRequest.addListener(
callback, filter, opt_extraInfoSpec);
Each addListener() call takes a mandatory callback function as
the first parameter. This callback function is passed a dictionary containing
information about the current URL request. The information in this dictionary
depends on the specific event type as well as the content of
opt_extraInfoSpec.
If the optional opt_extraInfoSpec array contains the string
'blocking' (only allowed for specific events), the callback
function is handled synchronously. That means that the request is blocked until
the callback function returns. In this case, the callback can return a
webRequest.BlockingResponse that determines the further
life cycle of the request. Depending on the context, this response allows
cancelling or redirecting a request (onBeforeRequest), cancelling a
request or modifying headers (onBeforeSendHeaders,
onHeadersReceived), and cancelling a request or providing
authentication credentials (onAuthRequired).
If the optional opt_extraInfoSpec array contains the string
'asyncBlocking' instead (only allowed for
onAuthRequired), the extension can generate the
webRequest.BlockingResponse asynchronously.
The webRequest.RequestFilter
filter allows limiting the requests for which events are
triggered in various dimensions:
- URLs
- URL patterns such as
*://www.google.com/foo*bar. - Types
- Request types such as
main_frame(a document that is loaded for a top-level frame),sub_frame(a document that is loaded for an embedded frame), andimage(an image on a web site). See webRequest.RequestFilter. - Tab ID
- The identifier for one tab.
- Window ID
- The identifier for a window.
Depending on the event type, you can specify strings in
opt_extraInfoSpec to ask for additional information about the
request. This is used to provide detailed information on request's data only
if explicitly requested.
Implementation details
Several implementation details can be important to understand when developing an extension that uses the web request API:
Conflict resolution
In the current implementation of the web request API, a request is considered
as cancelled if at least one extension instructs to cancel the request. If
an extension cancels a request, all extensions are notified by an
onErrorOccurred event. Only one extension is allowed to redirect a
request or modify a header at a time. If more than one extension attempts to
modify the request, the most recently installed extension wins and all others
are ignored. An extension is not notified if its instruction to modify or
redirect has been ignored.
Caching
Chrome employs two caches — an on-disk cache and a very fast in-memory
cache. The lifetime of an in-memory cache is attached to the lifetime of a
render process, which roughly corresponds to a tab. Requests that are answered
from the in-memory cache are invisible to the web request API. If a request
handler changes its behavior (for example, the behavior according to which
requests are blocked), a simple page refresh might not respect this changed
behavior. To make sure the behavior change goes through, call
handlerBehaviorChanged() to flush the in-memory cache. But don't do
it often; flushing the cache is a very expensive operation. You don't need to
call handlerBehaviorChanged() after registering or unregistering an
event listener.
Timestamps
The timestamp property of web request events is only guaranteed to
be internally consistent. Comparing one event to another event will give
you the correct offset between them, but comparing them to the current time
inside the extension (via (new Date()).getTime(), for instance)
might give unexpected results.
Error handling
If you try to register an event with invalid arguments, then a JavaScript error will be thrown, and the event handler will not be registered. If an error is thrown while an event is handled, or if an event handler returns an invalid blocking response, an error message is logged to your extension's console and the handler is ignored for that request.
Examples
The following example illustrates how to block all requests to
www.evil.com:
chrome.webRequest.onBeforeRequest.addListener(
function(details) {
return {cancel: details.url.indexOf("://www.evil.com/") != -1};
},
{urls: ["<all_urls>"]},
["blocking"]);
As this function uses a blocking event handler, it requires the "webRequest" as well as the "webRequestBlocking" permission in the manifest file.
The following example achieves the same goal in a more efficient way because
requests that are not targeted to www.evil.com do not need to be
passed to the extension:
chrome.webRequest.onBeforeRequest.addListener(
function(details) { return {cancel: true}; },
{urls: ["*://www.evil.com/*"]},
["blocking"]);
The following example illustrates how to delete the User-Agent header from all requests:
chrome.webRequest.onBeforeSendHeaders.addListener(
function(details) {
for (var i = 0; i < details.requestHeaders.length; ++i) {
if (details.requestHeaders[i].name === 'User-Agent') {
details.requestHeaders.splice(i, 1);
break;
}
}
return {requestHeaders: details.requestHeaders};
},
{urls: ["<all_urls>"]},
["blocking", "requestHeaders"]);
For more example code, see the web request samples.
Summary
Types
ResourceType
| Enum |
|---|
"main_frame",
"sub_frame",
"stylesheet",
"script",
"image",
"font",
"object",
"xmlhttprequest",
"ping",
"csp_report",
"media",
"websocket",
or "other"
|
OnBeforeRequestOptions
| Enum |
|---|
"blocking",
"requestBody",
or "extraHeaders"
|
OnBeforeSendHeadersOptions
| Enum |
|---|
"requestHeaders",
"blocking",
or "extraHeaders"
|
OnSendHeadersOptions
| Enum |
|---|
"requestHeaders",
or "extraHeaders"
|
OnHeadersReceivedOptions
| Enum |
|---|
"blocking",
"responseHeaders",
or "extraHeaders"
|
OnAuthRequiredOptions
| Enum |
|---|
"responseHeaders",
"blocking",
"asyncBlocking",
or "extraHeaders"
|
OnResponseStartedOptions
| Enum |
|---|
"responseHeaders",
or "extraHeaders"
|
OnBeforeRedirectOptions
| Enum |
|---|
"responseHeaders",
or "extraHeaders"
|
OnCompletedOptions
| Enum |
|---|
"responseHeaders",
or "extraHeaders"
|
OnErrorOccurredOptions
| Enum |
|---|
"extraHeaders"
|
RequestFilter
| properties | ||
|---|---|---|
| array of string | urls |
A list of URLs or URL patterns. Requests that cannot match any of the URLs will be filtered out. |
| array of ResourceType | (optional) types |
A list of request types. Requests that cannot match any of the types will be filtered out. |
| integer | (optional) tabId | |
| integer | (optional) windowId | |
HttpHeaders
BlockingResponse
| properties | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| boolean | (optional) cancel |
If true, the request is cancelled. This prevents the request from being sent. This can be used as a response to the onBeforeRequest, onBeforeSendHeaders, onHeadersReceived and onAuthRequired events. |
||||||
| string | (optional) redirectUrl |
Only used as a response to the onBeforeRequest and onHeadersReceived events. If set, the original request is prevented from being sent/completed and is instead redirected to the given URL. Redirections to non-HTTP schemes such as |
||||||
| HttpHeaders | (optional) requestHeaders |
Only used as a response to the onBeforeSendHeaders event. If set, the request is made with these request headers instead. |
||||||
| HttpHeaders | (optional) responseHeaders |
Only used as a response to the onHeadersReceived event. If set, the server is assumed to have responded with these response headers instead. Only return |
||||||
| object | (optional) authCredentials |
Only used as a response to the onAuthRequired event. If set, the request is made using the supplied credentials.
|
||||||
UploadData
| properties | ||
|---|---|---|
| any | (optional) bytes |
An ArrayBuffer with a copy of the data. |
| string | (optional) file |
A string with the file's path and name. |
FormDataItem
Since Chrome 66.
IgnoredActionType
| Enum |
|---|
"redirect",
"request_headers",
"response_headers",
or "auth_credentials"
|
Properties
20 |
chrome.webRequest.MAX_HANDLER_BEHAVIOR_CHANGED_CALLS_PER_10_MINUTES |
The maximum number of times that handlerBehaviorChanged can be called per 10 minute sustained interval. handlerBehaviorChanged is an expensive function call that shouldn't be called often.
|
Methods
handlerBehaviorChanged
chrome.webRequest.handlerBehaviorChanged(function callback)
Needs to be called when the behavior of the webRequest handlers has changed to prevent incorrect handling due to caching. This function call is expensive. Don't call it often.
| Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|
| function | (optional) callback |
If you specify the callback parameter, it should be a function that looks like this: function() {...};
|
Events
onBeforeRequest
Fired when a request is about to occur.
addListener
chrome.webRequest.onBeforeRequest.addListener(function callback)
| Parameters | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| function | callback |
The callback parameter should be a function that looks like this: function(object details) {...};
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
onBeforeSendHeaders
Fired before sending an HTTP request, once the request headers are available. This may occur after a TCP connection is made to the server, but before any HTTP data is sent.
addListener
chrome.webRequest.onBeforeSendHeaders.addListener(function callback)
| Parameters | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| function | callback |
The callback parameter should be a function that looks like this: function(object details) {...};
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
onSendHeaders
Fired just before a request is going to be sent to the server (modifications of previous onBeforeSendHeaders callbacks are visible by the time onSendHeaders is fired).
addListener
chrome.webRequest.onSendHeaders.addListener(function callback)
| Parameters | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| function | callback |
The callback parameter should be a function that looks like this: function(object details) {...};
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
onHeadersReceived
Fired when HTTP response headers of a request have been received.
addListener
chrome.webRequest.onHeadersReceived.addListener(function callback)
| Parameters | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| function | callback |
The callback parameter should be a function that looks like this: function(object details) {...};
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
onAuthRequired
Fired when an authentication failure is received. The listener has three options: it can provide authentication credentials, it can cancel the request and display the error page, or it can take no action on the challenge. If bad user credentials are provided, this may be called multiple times for the same request. Note, only one of 'blocking' or 'asyncBlocking' modes must be specified in the extraInfoSpec parameter.
addListener
chrome.webRequest.onAuthRequired.addListener(function callback)
| Parameters | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| function | callback |
The callback parameter should be a function that looks like this: function(object details, function asyncCallback) {...};
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
onResponseStarted
Fired when the first byte of the response body is received. For HTTP requests, this means that the status line and response headers are available.
addListener
chrome.webRequest.onResponseStarted.addListener(function callback)
| Parameters | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| function | callback |
The callback parameter should be a function that looks like this: function(object details) {...};
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
onBeforeRedirect
Fired when a server-initiated redirect is about to occur.
addListener
chrome.webRequest.onBeforeRedirect.addListener(function callback)
| Parameters | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| function | callback |
The callback parameter should be a function that looks like this: function(object details) {...};
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
onCompleted
Fired when a request is completed.
addListener
chrome.webRequest.onCompleted.addListener(function callback)
| Parameters | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| function | callback |
The callback parameter should be a function that looks like this: function(object details) {...};
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
onErrorOccurred
Fired when an error occurs.
addListener
chrome.webRequest.onErrorOccurred.addListener(function callback)
| Parameters | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| function | callback |
The callback parameter should be a function that looks like this: function(object details) {...};
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
onActionIgnored
Since Chrome 70.
Fired when an extension's proposed modification to a network request is ignored. This happens in case of conflicts with other extensions.
addListener
chrome.webRequest.onActionIgnored.addListener(function callback)
| Parameters | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| function | callback |
The callback parameter should be a function that looks like this: function(object details) {...};
|
|||||||||
