Important: Chrome will be removing support for Chrome Apps on Windows, Mac, and Linux. Chrome OS will continue to support Chrome Apps. Additionally, Chrome and the Web Store will continue to support extensions on all platforms. Read the announcement and learn more about migrating your app.
In-App Payments with Payments Merchant Account and the Chrome Web Store API
You can use a Payments Merchant Account and the Chrome Web Store API to sell virtual goods within your Chrome App or Chrome Extension.
The Chrome Web Store Developer Dashboard makes it easy to easy to create and manage virtual goods. You can provide localized descriptions for each product and offer items in local currencies. It also can help you to verify and manage licenses for the virtual goods purchased by each user.
In order to sell virtual goods, you'll need to:
- Create a Google Payments Merchant account.
- Create the items you wish to sell via the Developer Dashboard in the Chrome Web Store.
-
Include the appropriate
buy.jsfile in your package. - Wire up the sales flow.
The buy.js
file provides four functions:
google.payments.inapp.getSkuDetails- Returns an array of active items provided by your product from the Chrome Web Store. Maps to the Web Store API In-App Products List Method.
google.payments.inapp.buy- Purchases an item.
google.payments.inapp.getPurchases- Returns an array of items purchased by the user. Maps to the Web Store API Payments List Method.
google.payments.inapp.consumePurchase- Consumes an item.
Note: See Payments: Regions, fees and tiers for more information about fees and locations where you can sell your virtual goods.
Purchase flow
You can use google.payments.inapp.getSkuDetails to get the list
of available products, and then show those to the user.
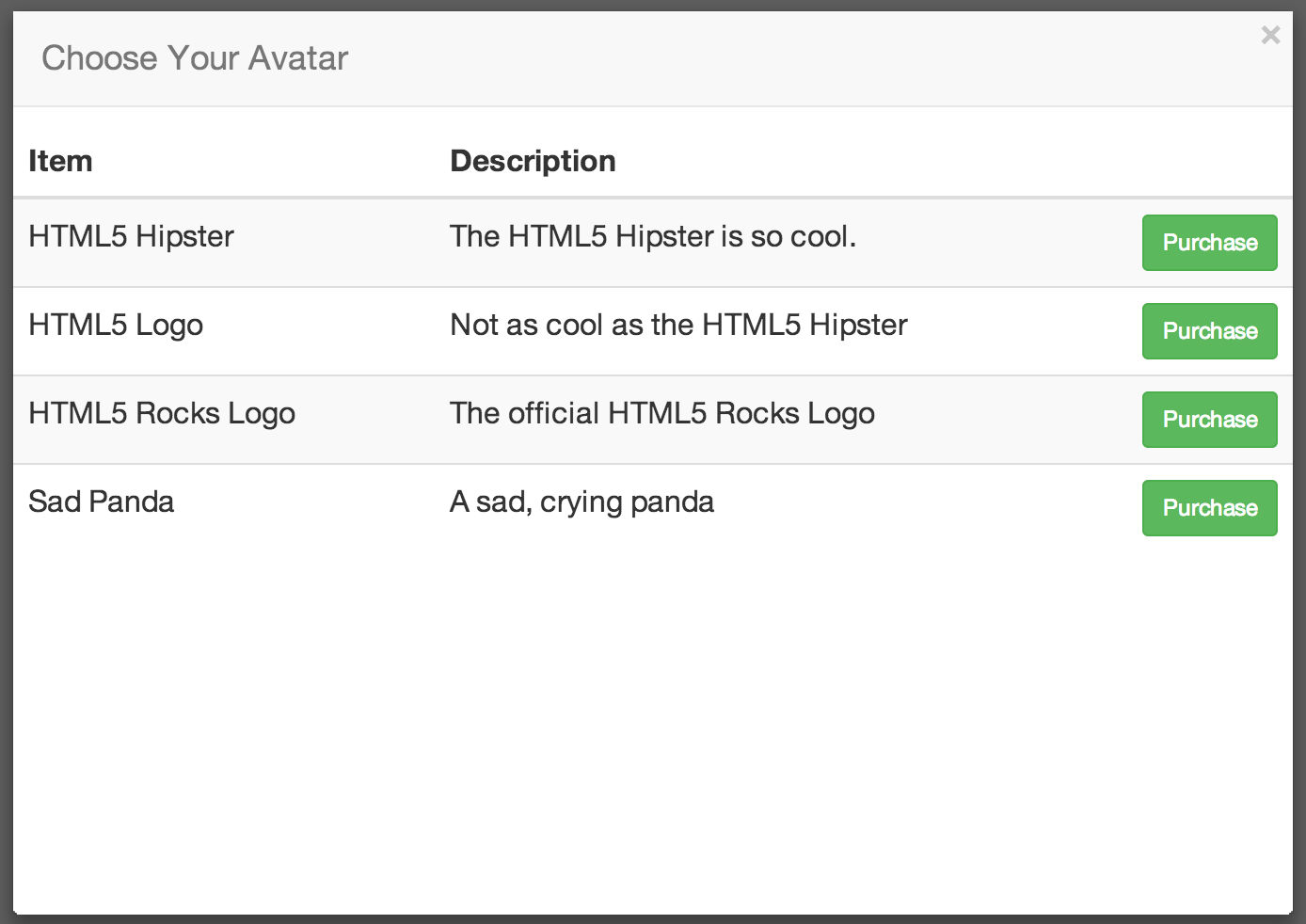
Best Practice: Before showing the user all of the items
that are available, compare the list of items that they've already purchased
(using google.payments.inapp.getPurchases) and provide some
indication that the items have already been purchased.
When a customer clicks a Purchase button within your Chrome App or Extension, Chrome uses the Google account of the user signed into Chrome to display the Google payment processing window.
When the user clicks the Accept and Buy button in the payment
processing window,
the Google payment server processes the payment and displays a purchase
confirmation dialog to the user.
The success or failure
callback is invoked appropriately.
Items uploaded to the Web Store are unable to be purchased through the same developer account. Instead, use a trusted tester account to run a trial purchase flow.
Note: if the user doesn't have a Google account, they are taken through the sign-up flow.
Using the Chrome Web Store API for In-App Purchases
The Chrome Web Store (CWS) API can be used to handle in-app purchases without the use of any server-side coding as was previously required by the deprecated Google Wallets for Digital Goods API.
- The Chrome Web Store handles the list of virtual goods available for sale, eliminating the need to create, store, or manage JSON Web Tokens.
-
You can get the list of available virtual goods through the
getSkuDetailsfunction. -
You must include the
buy.jslibrary with your package, and load the library from its location in your package. -
You must call the
buy()method with an extra parameter calledparameters. - The UI to process payments is displayed in a separate window, rather than in an iframe.
-
The Chrome Web Store manages the list of purchased virtual goods
(licenses) for each user and exposes that list to you through
the
getPurchases()function.
Setting up your account
In order to use the Chrome Web Store API to handle in-app purchases, you'll need to create a Google Payments Merchant account.
Once you’ve created the Merchant account, it will be automatically associated with your Chrome App or Extension listing in the Chrome Web Store.
Creating and Managing your virtual goods
Before you can sell any virtual goods, you need to create the list of in-app products that are available for purchase. The Chrome Web Store simplifies this process for us by providing an interface for creating in-app products and licenses. This interface can be found in the In-app Products tab in the Chrome app listing page of the Chrome Web Store Developer Dashboard. Once you have created your in-app products, you can continue to use this interface to manage them.
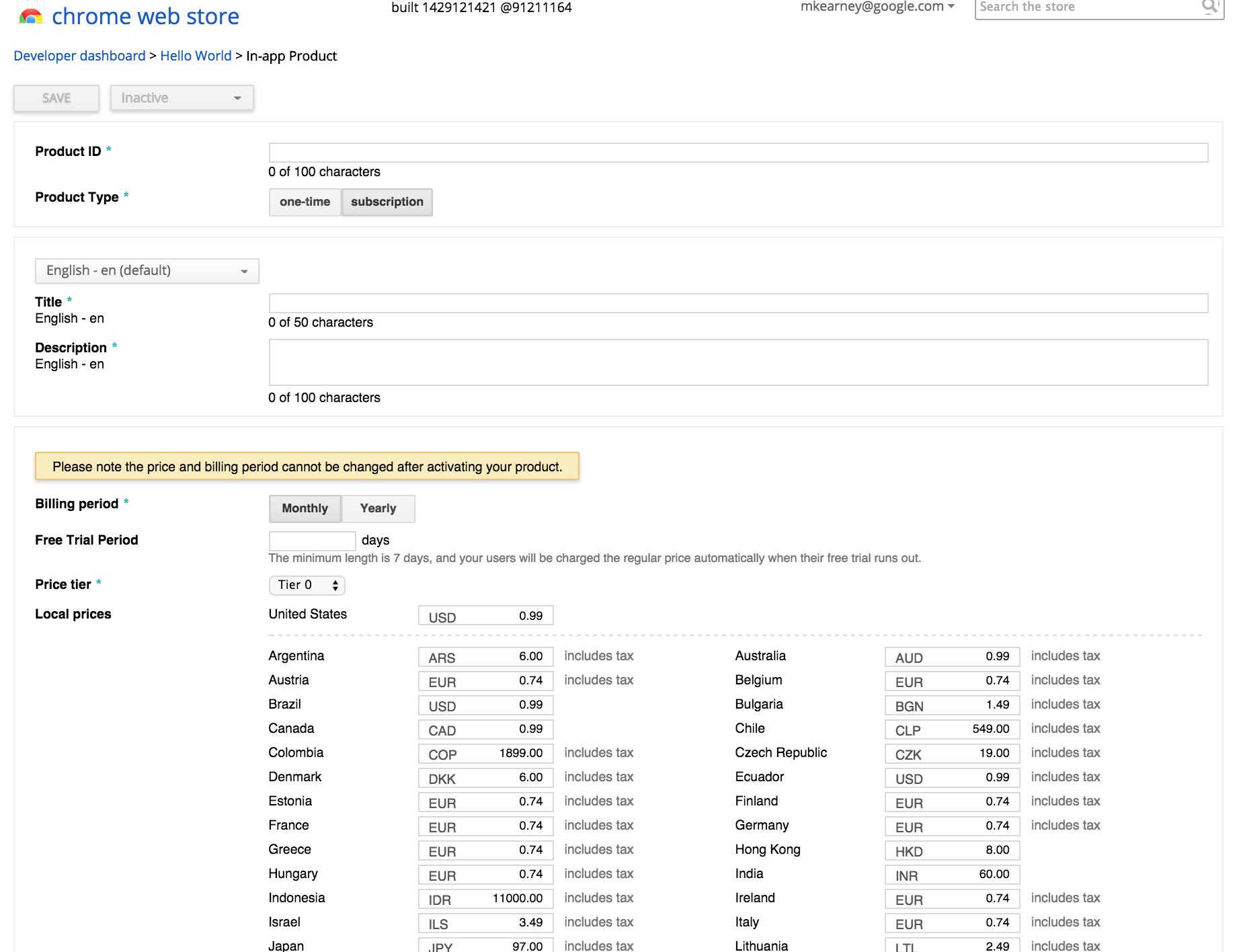
- Open the Chrome Web Store Developer Dashboard and edit the listing for your app.
- Switch to the In-app Products tab at the top of the page.
- Click Add new product.
-
Provide the necessary information:
- Product ID
- An identifier (SKU) you'll use to identify that specific product. Product IDs must start with a lowercase letter or number and can only contain lowercase letters(a-z), numbers(0-9), dots(.) and underscores(_).
- Title
- A friendly name of your product that will be shown to users on the purchase confirmation page.
- Description
- A short description of the item that will be shown to users on the purchase confirmation page.
- Choose the price tier or create a custom price within the tier range that you wish to sell the item for.
- Click Save to save the item.
- Activate by changing the state to Active.
If you want to prepare digital goods for release on a specific day, you
can leave the state set to Inactive until you're ready to
make those available. This means you can launch new features or levels,
but keep them hidden until you're ready.
- You can have up to 100 items (active, inactive, or archived) at any given time.
- You should move older items that are no longer for sale to archived.
- Be careful when deleting items as users may already have purchased them and may lose their license.
- Once a product ID has been used, it cannot be used again, even if it has been deleted.
Querying available items
The getSkuDetails function returns a list of all active
virtual
goods available from the Chrome Web Store available for purchase by the
user, including the product ID (SKU), title, description, and price.
You can provide an optional SKU argument to the function, which will then
return only the details for that specific item.
google.payments.inapp.getSkuDetails({
'parameters': {'env': 'prod'},
'success': onSkuDetails,
'failure': onSkuDetailsFail
});
Note: The parameters field is required and must be set to
{'env': 'prod'} to tell Chrome to use the production
instance of the API. Review the Testing your
app
section for details on how to test your app without incurring a charge.
You can learn about adding trusted testers when you
publish your app here.
The response will look like:
{
"response": {
"details": {
"kind": "chromewebstore#inAppProductList",
"inAppProducts": [
{
"kind": "chromewebstore#inAppProduct",
"sku": "70darkchocolate",
"item_id": "aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa",
"type": "inapp",
"state": "ACTIVE",
"prices": [
{
"valueMicros": "990000",
"currencyCode": "USD",
"regionCode": "US"
}
],
"localeData": [
{
"title": "Dark Chocolate (70%)",
"description": "The best chocolate available.",
"languageCode": "all"
}
]
},
{
...
}
]
}
}
}
You can find the full description of In-App Products Representation and Methods in the Web Store API Reference.
For example, you might want to list the details of each object you get back from the function:
function onSkuDetails(skus) {
var products = response.response.details.inAppProducts;
var count = products.length;
for (var i = 0; i < count; i++) {
addProductToUI(products[i]);
}
}
Responding to a purchase request
The following code snippet shows how to initiate the purchase flow for an item managed through the Chrome Web Store:
var sku = "giant_tv";
google.payments.inapp.buy({
'parameters': {'env': 'prod'},
'sku': sku,
'success': onPurchase,
'failure': onPurchaseFail
});
When the purchase completes, Chrome will call the defined callback with the a parameter that looks like:
{
"jwt": "eyJhb...0oFuU",
"request": {
"cartId": "00000000000000000000.0000000000000000000"
},
"response": {
"orderId": "00000000000000000000.0000000000000000000"
}
}
Verifying what items the user has purchased
If you want to verify that the user has purchased an item and has a
current license, you can call
google.payments.inapp.getPurchases. The function will always
return the most up to date information, and will reflect if the purchase
was cancelled by the user, or refunded through the
Payments Merchant console.
google.payments.inapp.getPurchases({
'parameters': {'env': 'prod'},
'success': onLicenseUpdate,
'failure': onLicenseUpdateFail
});
The Chrome Web Store will return the list of SKUs that the user has purchased:
{
"response": {
"details": [
{
"kind": "chromewebstore#payment",
"itemId": "aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa",
"sku": "giant_tv",
"createdTime": "1387221267248",
"state": "ACTIVE"
}
]
}
}
Note: See the Web Store API Reference for more details on the payment methods.
function onLicenseUpdate(licenses) {
var licenses = response.response.details;
var count = licenses.length;
for (var i = 0; i < count; i++) {
var license = licenses[i];
saveLicense(license);pay
}
}
Consume purchased item
If you want to consume an item that a user has purchased,
so that the user can purchase again,
you can call
google.payments.inapp.consumePurchase.
The function will change the license status
from "active" to "cancelled_by_developer".
google.payments.inapp.consumePurchase({
'parameters': {'env': 'prod'},
'sku': sku,
'success': onConsume,
'failure': onConsumeFail
});
After consuming a license, if you make a getPurchase call,
you'll get:
{
"response": {
"details": [
{
"kind":"chromewebstore#payment",
"itemId":"bgjmpalnjpigmmelcdiakkfofbofhege",
"sku":"bullet",
"createdTime":"1424800615789",
"state":"CANCELLED_BY_DEVELOPER"
}
]
}
}
Note: The consumePurchase API won't work with in-app subscriptions.
Subscriptions
Developers can also offer in-app subscriptions.
If a free trial is specified, users will go through the purchase flow for a 0 amount, and the first recurring order will occur automatically as soon as the free trial period expires. Note that once a subscription item is activated, developers can no longer inactivate it or change the price or period. However, the free trial period can be changed at any time. While non-subscription items will have the type “inapp”, subscription items will have the type “subs”. For example, getSkuDetails will return a result for a subscription item that resembles:
{
"kind":"chromewebstore#inAppProduct",
"sku":"banana",
"item_id":"bgjmpalnjpigmmelcdiakkfofbofhege",
"type":"subs",
"state":"ACTIVE",
"prices":[{"valueMicros":"990000","currencyCode":"USD","regionCode":"US"}],"localeData":[{"title":"Bullet","description":"a bullet","languageCode":"en-US"}
Testing purchases
Prior to publishing your app to the world, you can test the In-App Payment experience by publishing it only to trusted testers. When your app is published to trusted testers, the purchase flow will proceed normally, except they will not be charged.
Sample Chrome App
For a simple app that demonstrates how to use CWS API for in-app products, you can download the source code here.
Note, this app is not published in the Chrome Web Store to prevent accidental purchases.
